Planning the installation process thoroughly and having all the necessary information on hand before installing SQL Server 2005, 2008, 2012, 2016, and above is crucial.
- Hardware and software requirements
- Version and edition of SQL Server
- License details of SQL Server
- Name of SQL Server
- Components to be installed
- Authentication mode of SQL Server
- Service accounts and collection of SQL Server
- Location of Binary files and Database files
Hardware requirements
512MB of RAM (1 GB recommended)
750 MB of Hard disk Space to install all SQL components (115 MB for Client tools)
Software requirements
- Windows Server 2000/2003/2008 with latest service pack
- Windows installer 3.0
- NET Framework 2.0
- SQL Native Client
- IIS if we are installing reporting services
- Internet explorer 6.0
SQL Server Evaluation Edition
All the features of the Enterprise Edition are available in the SQL Server Evaluation Edition, also known as the Trial Edition, but it is only valid for 180 days. During that time, the tools will still function, but the server services will cease.
SQL Server Developer Edition
The features of SQL Server Developer Edition are identical to those of SQL Server Enterprise Edition; however, it can only be used as a development and test system and cannot be used as a production server due to licensing restrictions. Students can download this version for free as part of Microsoft’s DreamSpark initiative.
SQL Server Enterprise Edition
The full-featured version of SQL Server, known as SQL Server Enterprise Edition, comes with a variety of tools for setting up and maintaining a SQL Server cluster in addition to the main database engine and add-on services.
SQL Server Standard Edition
The stand-alone services and the main database engine are included in the SQL Server Standard edition. It is different from the Enterprise edition in that it does not have some high-availability features like parallel indexes and hot-add memory, which allow memory to be added while the server is still operating, and it supports fewer active instances (the total number of nodes in a cluster)
SQL Server Express Edition
The core database engine of SQL Server is included in the free, scaled-down edition known as SQL Server Express Edition. It is restricted to using one processor, one gigabyte of RAM, and four gigabytes of database files (10 GB of SQL Server database files), even though there are no restrictions on the number of databases or users that can be supported.
Name of SQL Server
It is not necessary for a client to specify the instance name in order to establish a connection when SQL Server is installed in the default instance. All that is required of the client is the server’s name.
When you specify an instance name during installation, it is combined with the computer’s network name to identify a named instance. When connecting, the client needs to provide the name of the instance as well as the server.
Components to be installed:
SQL Server has a fully integrated setup through which all components can be installed together via a single installation.
1. SQL Server Database Services.
2. Analysis services
3. Reporting services.
4. Integration services.
5. Workstation components. Books online and development tools.
Depending on the Microsoft SQL Server components you choose to install, The following 10 services
6.Service Accounts:
To function, all SQL Server services need a login account. This account can be a local system account, a network service account, a domain user account, or a local service account.
Local service, or built-in, is a low-privilege service account, while local system accounts have high privileges.
7.Collation: A collation determines the rules under which character data is stored and compared. SQL Server has two groups of collations: the Windows collation and the SQL Server collation.
By default Windows collation, if your application requires old version collation, then SQL collation can be selected.
8. Location of Binary files and Database files
Default Drive locations for files C:\ Binary files
D:\ Data files
E:\ Log files
T:\ Tempdb files
Y:\ System DB files
X: Backup files

Sp_configure ‘show advanced options’,1/0
Reconfigure with override
1. Enable the service
0-Disable the service
To verify SQL Server product details, we can use the below commands.
SELECT @@VERSION (OR)
SELECT
SERVERPROPERTY(‘Edition’) AS ‘Edition’, SERVERPROPERTY(‘ProductVersion’) AS ‘ProductVersion’, SERVERPROPERTY(‘ProductLevel’) AS ‘ProductLevel’,
SERVERPROPERTY(‘ResourceLastUpdateDateTime’) AS ‘ResourceLastUpdateDateTime’, SERVERPROPERTY(‘ResourceVersion’) AS ‘ResourceVersion’
Hotfix:
A hotfix is a piece of code, also known as a patch, that addresses a bug in a product. Customers of the products can receive email notifications or visit a software vendor’s website to learn about the latest hotfixes and download the ones they want to use.
Service pack
Hotfixes are sometimes packaged as a set of fixes called a combined hotfix or a service pack.
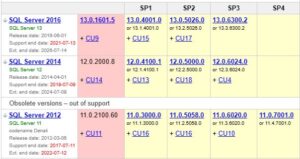
Best practices for installing service packs, cumulative updates and hotfixes for SQL Server
- Test on a test/dev SQL server first, and only after you have confirmed that all applications are working as expected can you install it on a production SQL server.
- Run DBCC CHECKDB on ALL databases (user and system databases) and ensure that there are no errors reported.
- Backup all databases (user and system databases) and full-text catalogs (if applicable). This is not required, but highly recommended.
- Stop Monitoring and Anti-virus services
- Make sure you have the proper permissions to install (administrative privilege on server)
After installing, Reboot the Server and verify the service pack has applied successfully for SQL Server
Uninstalling Service packs
using SQL Server 2008 onward. We can simply remove any installed updates, so let’s look at how to remove only your service pack without wiping out your SQL Server instance!
Steps for Uninstalling Service pack
- Backup of user and system databases and scripts for all login and users
- Using Add or Remove Programs, database administrators can uninstall SQL Server 2008 service packs.
- In Add or Remove Program, select the Show Updates check box, then choose Service Pack 1 for SQL Server 2008, which comes under Microsoft SQL Server 2008, and click the Remove button to begin the uninstallation process.
- This will open up Uninstall Service Pack 1 for SQL Server 2008/2012.
In the Select Features screen, you can choose the feature from which you want to remove the update. Click Next to continue with the uninstallation process. - On Complete screen, you will be able to see the message Your SQL Server 2008/2012 remove update operation has been completed successfully. You can also verify the uninstallation process activities by going through the summary log.
- Click Close to end the uninstallation process. You can verify the SQL Server 2008/2012 product version by executing the below-mentioned query in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
YES, this intelligible message