The Server Log Shipping feature automates the backup of transaction log files from a primary database on a primary server instance to one or more secondary databases on separate secondary server instances. The transaction log backups are applied to each of the secondary databases separately. A third server instance, known as the monitor server, optionally monitors the history and status of backup and restoration operations and, optionally, raises alerts if these operations fail to proceed as scheduled.
It is a H.A. + D.R concept
Pre-requisites:
1. All log shipping servers should have the same case-sensitivity settings
2. In a log shipping arrangement, the databases must use the full recovery model or the bulk-logged recovery model
3. To enable log shipping, you must be a sysadmin on each server instance
4. Two shared folders with read/write or full access to SQL service accounts (a backup folder on the primary server and a copy folder on the secondary server)
Terminology:
- Primary Server : The primary server includes the source database for transmitting transactional logs to the production server
- Primary database: The target database for the transactional logs is located on the secondary server
- Secondary Server: The primary server’s database that you wish to backup to another server
- Secondary database: A warm standby copy of the primary database’s secondary database, which can be in either a recovering or instandby condition
- Monitor server: The monitor server maintains logshipping job information and gives alarms in the event of a failure.(Or)
It is an optional instance of SQL Server that tracks all logshipping details, such as copy jobs, restoration jobs, and backup job history
Backup Folder:This backup folder is a shared folder on the primary server. Every log backup file will be saved according to the time period specified. Save this file with the extension.trn
- Copy Folder:This copy folder is a shared folder on the secondary server. It may be present on the secondary server, but data restoration will be slow due to network issues.These files are saved with the extension.trn
- Restore:It collects log files from the copied folder and sends them to the secondary server (the database engaged in log shipping)
- Alerts:Alerts are generated whenever a backup, copy, or restore job fails. During the scheduled time period
- TUF: Transactional undo file:It is created at the time when you are restoring the database with standby mode
- The Tuf file is created at the target [secondary] server database file location with the Tuf extension
- In standby mode, while restoring the log backup, all uncommitted transactions are logged to the undo file, with just committed transactions stored on disc, allowing users to browse the database
- So, when we restore the next transaction log backup, SQL Server will collect any uncommitted transactions from the undo file and compare them to the new transaction log backup to see if they are configured (or not)
- .WRK:
This.wrk file is created when data is copied (in progress) from the backup folder (primary server) to the copy folder (secondary server). Once the copying is complete, the file extension will be marked as.trn
How log-shipping will work:
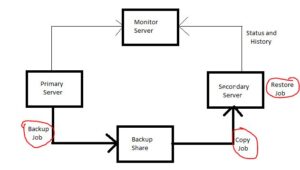
- Log shipping is made up of three steps:
1. Create a backup of the transaction log on the primary server instance
2. Transfer the transaction log file to the secondary server instance
3. On the secondary server instance, restore the log backup - A log-shipping configuration does not fail over from the primary server to the secondary server automatically. If the primary database fails, any of the secondary databases can be manually brought online
- we can use a secondary database for reporting purposes
- The backup job is conducted by the primary server instance to backup the transaction log on the primary database, and it saves the log backup in the backup folder. The backup folder in this diagram is in a shared directory; the backup share
- Each secondary server instance executes its own copy task, which copies the primary log-backup file to its own local destination folder
- Each secondary server instance does its own restore operation in order to restore the log backup from the local destination folder to the secondary database
- The primary and secondary server instances communicate with the monitor server instance by sending their own history and status
Error Message:
1. Error 14420: This warning is displayed when a backup job fails
2. Error 14421: This message will appear if the restore fails
Disadvantages:
1) There may be some data loss.
2) we must bring the secondary server database online manually because automatic failover is not available.
3) We need at least 15-20 minutes to get secondary online
Advantages:
1) Only log shipping allows you to have a secondary database on standby
2) So you can use it for reporting purposes
3) We can maintain many secondary standby servers, which means just one primary number of secondary servers
4) No additional software or hardware is required
5) Its upkeep is simple
Note:
1) It has the ability to switch from a full recovery model to a bulk recovery model
2) However, it should not switch from a full recovery model to a simple recovery model
3) We can arrange the secondary server database to be norecovery or standby in the same version
4) We can configure the secondary server database as a standby state in different versions
5) We manually transferred the logs from the primary server to the secondary server
The following are some prevalent scenarios:
Scenario 1: Renaming the database
- Primary server is not advised because the entire connection would fail.
- Secondary (standby or no recovery): We cannot perform it
Scenario 2: Adding a file and a File group
- Disable all jobs (otherwise you will receive continual alerts)
- Add the file to the primary server
- Take the log backup
- Restore the secondary server with the move option
- Start the jobs
Scenario 3: file moving from one location to another location
- a) Primary server:
1) Disable all the jobs
2) Find the logical path of the files
3) Please execute alter database command
4) Bring the database offline
5) Move the files from old location to new location and rename or delete the old location file
6) Bring the database online
7) Finally, enable the jobs
B) Secondary Server
(The secondary database should be in norecovery; otherwise, we can’t move tiles)
1) Disable all the jobs
2) Find the logical path of the files in the database
3) Please execute alter database command
4) Stop the instance
5) Move the files from old location to new location and rename or delete
6) Bring the instance online
7) Enable the jobs
Scenario 4: switch over or smoke test
1. Ensure that all backup files have been copied and restored completely from the primary to secondary servers
2. Disable all jobs (backup, copy, and restore)
3. Obtain the login information
4. Use the tail log backup with no recovery to restore the database
Backup log hari to disk=’G:Copy Folderlog_0547n’ with norecovery
5. Restore in the secondary server using recovery
Restore log hari_new from disc G:Copy Folderlog 0547.trn’ with recovery
6. Verify all logins with the primary server
7. If we come across an orphan user, we just fix it
8. Inform the client that the connection will be redirected to the alternative server
Scenario 5: Physical and logical renaming
It is feasible on the primary server but not on the secondary server
Scenario 7: Offline or online
1. On the primary server, we can bring the database offline and online
2. We can bring the database offline and online on the secondary server, but it should only be in standby mode
Useful Commands for Log Shipping Details:
Execute these commands on the primary server
Select * from: sdb.log shipping primary_databases
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_monitor primary
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_monitor_alert
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_monitor_error_detail
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_monitor_history_detail
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_primary_secondaries
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_primaries
Execute these commands on the secondary server
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_monitor_alert
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_monitor_error_detail
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_monitor_history_detail
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_monitor_secondary
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_secondaries
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_secondary
Select * from msdb..log_shipping_secondary_databases
Useful stored procedures for log shipping maintenance:
1. sp_add_log_shipping_primary_secondary : This stored procedure creates an entry for a secondary database on the primary server
2. Sp_delete_log_shipping_primary_database : This stored procedure deletes the primary database’s log shipping, including backup jobs and local and remote histories
Use this stored procedure only after you have removed the secondary databases using Sp_delete_logshipping_primary_secoundary (which removes the entry for a secondary database on the primary server).
4. Sp remove log shipping alert_job: Removes an alert job from the log shipping monitor server if the job exists and there are no longer primary or secondary databases to be watched
5. Sp_delete_logshipping_secondary_database : This stored procedure deletes a secondary database as well as the local and remote history
6. Sp_deletedog_shipping_secondary_primary : This stored procedure deletes information about the selected primary server from the secondary server, as well as the secondary’s copy and restore jobs