Records->Pages->Extents->Files->Database
Pages:The SQL Server page size is 8 KB. This translates to 128 pages per megabyte for SQL Server databases. Each page starts with a 96-byte header that contains system information about the page. This information includes the page number, page type, page size, and the allocation unit ID of the object that owns the page.
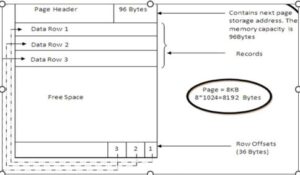
A row offset table begins at the end of the page, and each row offset table contains one item for each row on the page. Each entry indicates how far the first byte of the row is from the beginning of the page.
As we should know, the following are some of the data pages that can be saved in SQL Server:
Managing Extent Allocations
Global Allocation Map (GAM): GAM pages keep track of which extents have been assigned. Each GAM encompasses 64,000 extents, or over 4 GB of data. Each extent in the interval covered by the GAM has one bit. If the bit is 1, the extent is unallocated; if the bit is 0, the extent is assigned.
Shared Global Allocation Map (SGAM): SGAM pages keep track of which extents are currently being used as mixed extents and which pages are currently unused. Each SGAM contains 64,000 extents of data, or nearly 4 GB. In the interval it covers, the SGAM has one bit for each extent. If the bit is 1, the extent is mixed and has a free page. If the bit is set to 0, the extent is not used as a mixed extent, or it is utilised as a mixed extent with all of its pages used.
Tracking Free Space
Page Free Space (PFS) pages track the allocation status of each page, whether an individual page has been allocated, and the amount of free space on each page. The PFS has one byte for each page that records if the page is allocated and, if so, whether it is empty, 1 to 50% full, 51 to 80% full, 81 to 95% full, or 96 to 100% full.
Boot Page: There is one unique data page per database. It is the database’s initialization page. The database boot page is always saved on page 9 of file 1, the primary file group’s initial file.
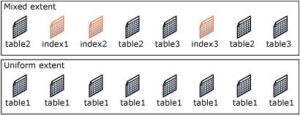
Pages from various extents are often assigned to a new table or index. When a table or index has eight pages, it changes to using uniform extents for additional allocations. When you establish an index on an existing table with enough rows to fill eight pages, all allocations to the index are in uniform extents.
Extents:
Extents are the basic unit for managing space. An extent is defined as eight physically contiguous pages, or 64 KB. This means SQL Server databases have 16 extents per megabyte.
A single object owns uniform extents; all eight pages in the extent can only be utilised by the owning object.
Up to eight objects can share mixed extents. Each of the extent’s eight pages can be held by a distinct object.